In the first 16 days of June, Ethereum has posted over 750k failed transactions, during which users have spent thousands in Gas fees.
Contents
766,432 Transactions Failed in Ethereum
According to Blockchair data—a blockchain explorer, there are currently 766,432 failed transactions. This number keeps rising with every block since the network keeps processing transactions. For every failed transaction, miners are paid processing fees in Gas. As a result, despite the transaction not going through, the sender must part with their hard-earned funds.
That users have to pay Gas fees even when transactions don’t go through is according to how Ethereum is designed. Part of this is to guarantee the integrity of the network. Second, it is a protective mechanism to shield the platform against spam executed through dust attacks.
Should Ethereum, a smart contracting platform whose demand for block space is at astronomical levels, be subjected to dust attacks where it is bombarded with spam transactions, it can be overwhelmed, forcing Gas fees even higher. In that case, transacting on Ethereum would be even more expensive.
Why Ethereum Transactions Fail
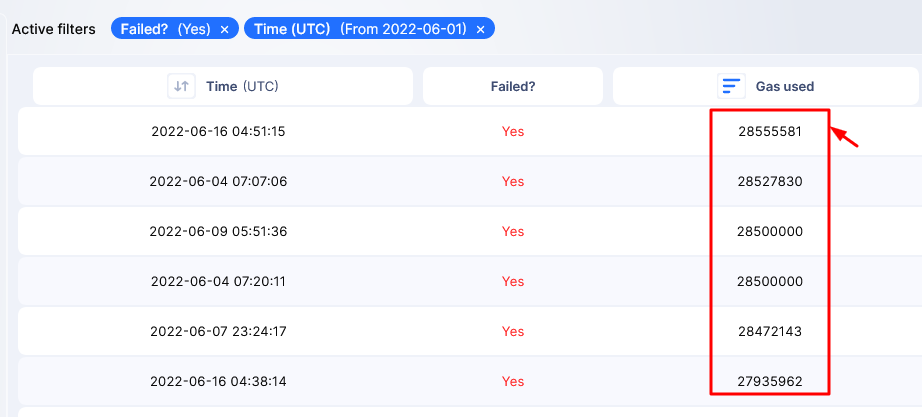
Typically, transactions in Ethereum fail if the wrong sender signs a transaction and a party attempts to send negative funds. Because Ethereum’s on-chain fees are not fixed and dynamic, the main reason why transactions fail is due to “negative funds” arising when funds send are less than current Gas fees. The highest amount of Gas spent by a user was 28555581, registered on June 16, 2022.
A notable observation is that Gas fees amount change depending on transactions. This is because, unlike Bitcoin and other transactional layers like Litecoin or Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum is a smart contracting network.
Depending on the complexity of the smart contract and transaction, fees can drastically vary to reflect the “fuel” needed to get the transaction through the network. The “heavier” or more complex a smart contract is, the higher the Gas fees, and vice versa.
Addressing Scalability and Lowering Gas Fees
However, Ethereum’s top brass are currently working on addressing high Gas fees.
The success of layer-2 solutions has partly alleviated the problem, but Gas fees remain relatively higher than competing platforms like Solana.
It's a big day for Ethereum.
— pastry (@PastryEth) June 8, 2022
Within the next 24 hours, the Ropsten network will undergo The Merge.
This marks the final phase of testing before deployment on mainnet.
Let's dive in… pic.twitter.com/X7GdZqoR8z
With the mainnet Merge expected in the months ahead, Ethereum developers expect better implementation of on-chain scaling solutions like sharding for lowering Gas fees.
Image Source
- ethereum feature image blockmagnates (1): Photo by Nenad Novaković on Unsplash






